Appearance
Tips: Ruby on Rails
Different ways to print
p: for debugging. For each object, directly writes obj.inspect followed by a newlineprint: low level, does not add new line or separator by defaultputs: like regular print in other languages
Array methods
Method Name Aliases
Array#filter === Array#selectArray#map === Array#collectArray#member? === Array.include?
Slicing
Array#toreturn the beginning of the array up to position (inclusive)Array#fromreturn the tail of the array from position (inclusive)Hash#sliceselect keys from a hash
Iterator
Array#eachHash#each.map.with_index- For example:
'abcd'.map.with_index {|x, i| x * i} #=> ["", "b", "cc", "ddd"]
- For example:
Empty/Nil/Blank/etc
#empty?- Ruby method; exists on Array, Set, Hash, String
- does not exist on all Enumerable
- on string: true iff it's empty string
#nil?- Ruby method; exists on Object class
- true iff it's nil
#blank?- Rails ActiveSupport method
- on string: true iff the string is whitespace only
- on array/set/hash: same as
#empty? trueis not blank,nil & falseare blank
#present?- opposite of
#blank?
- opposite of
#presence- return self if present, else nil
See also:
if obj.present?vsif obj- Rails ActiveSupport source code
- Differences Between #nil?, #empty?, #blank?, and #present?
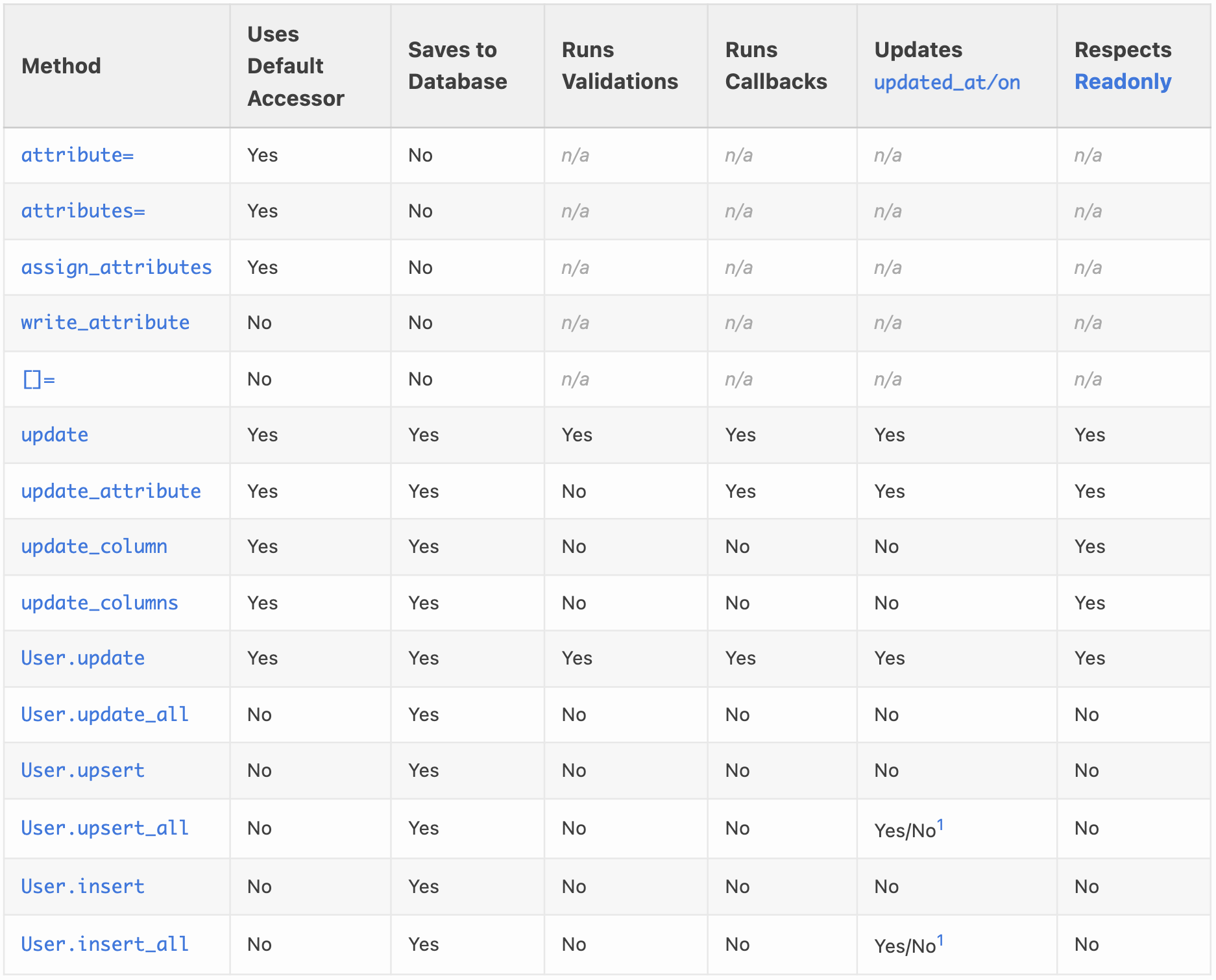
Different ways to update a record
hash literal punning
ruby shorthand hash syntax (punning in js) (ruby 3.1+)
ruby
a = 1
b = 2
{ a:, b: }
# => { a: 1, b: 2 }string/symbol as hash keys
ruby
{ abc: "key is a symbol" }
=== { :abc => "key is a symbol" }
=== { "abc": "key is a symbol" }
!== { "abc" => "key is a string" }Mandatory method keyword arguments
ruby
#You must name the keyword arg when calling this function
def action(amount:, reason: 'default value')
@amount = amount
@reason = reason
endVariables that starting with @
Class variable scoping
@@xxxclass variable@xxxinstance variable
meta programming
ruby
a = {}
# Get information of available functions
a.methods
a.method(:to_json)
a.method(:to_json).arity # get expected # of args
# Call a function
a.send(:slice, :key1, :key2)
== a.method(:slice).call(:key1, :key2)
# list all methods that ends with '?'
'abc'.methods.filter { |a| a.to_s.ends_with?('?') }attr_accessor
attr_accessorcan read and writeattr_readeronly read valueattr_writeronly assign value
https://www.rubyguides.com/2018/11/attr_accessor/
We want expose internal value to outside world
ruby
class Food
def initialize(protein)
@protein = protein
end
end
bacon = Food.new(21)
# You can define the following methods:
def protein
@protein
end
def protein=(value)
@protein = value
end
# OR simply have:
class Food
attr_accessor :protein
...
endclass static method syntax
ruby
class A
class << self
def method
...
end
end
end
is equivalent to
class A
def self.method
...
end
end